In the realm of automation and robotics, the selection of appropriate Servo Motors is a critical factor that can significantly influence the performance and efficiency of various projects and applications. Servo Motors are integral components that provide precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration, making them ideal for use in a wide range of fields, from industrial machinery to consumer electronics. With the market flooded with options, choosing the right Servo Motor can be a daunting task, requiring careful consideration of several technical specifications and operational requirements.
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of Servo Motors have expanded, offering greater precision and improved energy efficiency. Understanding key factors such as torque, speed, size, and compatibility with control systems is essential for engineers and hobbyists alike. Whether you're designing a robotic arm, an automated assembly line, or any other application that demands reliable motion control, having a solid grasp of how to evaluate Servo Motors will empower you to make informed decisions that enhance the overall effectiveness of your projects. In the following sections, we will delve into the essential criteria to consider when selecting Servo Motors tailored to your specific requirements, ensuring that your endeavors are both successful and innovative.

Servo motors are integral components in a wide range of automation and robotics applications, driven by precision and control. Understanding the fundamental concepts of servo motors begins with recognizing their primary function: to provide angular or linear position control. Unlike standard motors, servo motors can be precisely controlled to a specific position, making them ideal for tasks that require accuracy, such as robotic arms, CNC machinery, and automated assembly lines.
To grasp the mechanics behind servo motors, it's essential to familiarize oneself with key terms and components. The servo system typically consists of a motor, a controller, and a feedback mechanism. The motor converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, the controller dictates the desired position or speed, and the feedback mechanism, often a potentiometer or encoder, ensures accurate positioning by relaying information about the motor's current state back to the controller. This closed-loop system allows for precise adjustments, enabling applications that demand high levels of performance and reliability.
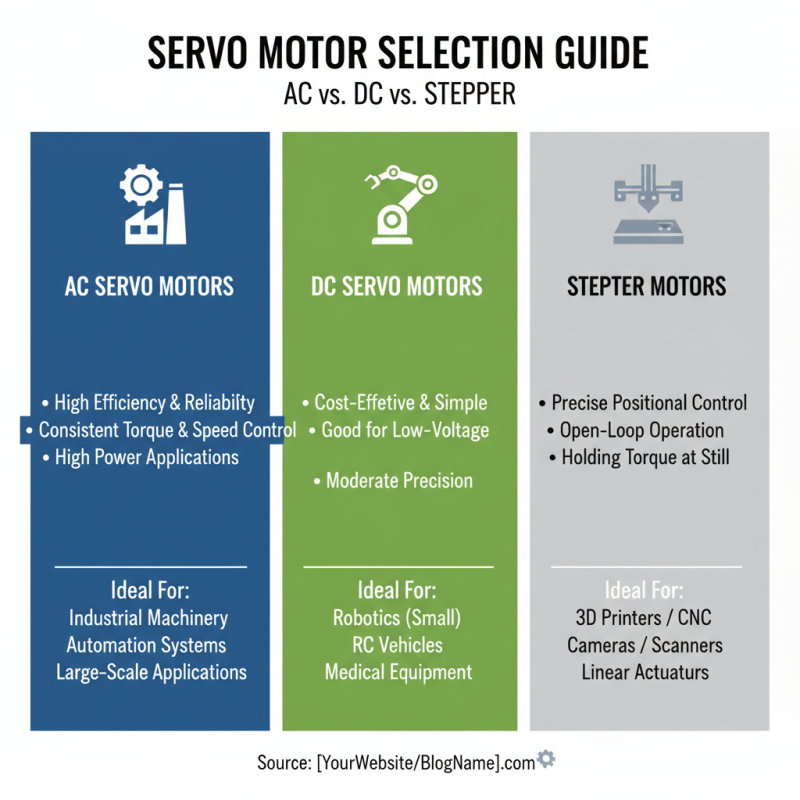
When selecting servo motors for your projects and applications, understanding the differences between AC, DC, and stepper motors is essential. AC servo motors are known for their high efficiency and reliability, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent torque and speed control. They are often utilized in industrial machinery and automation systems where precise movement over extended periods is crucial. Additionally, AC motors can handle higher power levels, which allows them to perform efficiently in larger-scale applications.
On the other hand, DC servo motors offer another set of advantages, particularly regarding their simplicity and ease of control. These motors usually provide excellent torque at low speeds, making them suitable for applications like robotics and small-scale automation where responsive movements are critical. Furthermore, DC motors generally require less complex drive electronics than their AC counterparts, which can be beneficial for smaller projects with budget constraints.
Stepper motors offer a unique solution for applications where precise positioning is required without the need for feedback systems. They move in discrete steps, allowing for exact positioning along with high reliability. This makes them ideal for 3D printing, CNC machines, and applications that involve direct control of movement without continuous rotation. While they might not deliver the smooth motion of AC or DC motors, their simplicity and precision often make them the go-to choice for tasks requiring accurate step control. By assessing the specific needs of your application, you can choose the right type of servo motor to optimize performance and efficiency.
When selecting servo motors for your projects, understanding the torque and speed requirements of your specific application is paramount. Torque, often measured in Newton-meters (Nm), is essential for determining how much load the motor can handle. Assessing the peak and continuous torque needed for your application will ensure that the servo motor can perform efficiently without overheating or stalling. Additionally, considering the torque curves across various speed ranges helps in selecting a motor that maintains optimal performance under different operational conditions.
Speed, measured in RPM (revolutions per minute), also plays a critical role in the selection process. The speed required depends on the nature of the application, whether it is robotics movement, CNC machinery, or industrial automation. It’s vital to understand the dynamics of your system, including the acceleration and deceleration phases, as well as the maximum inline speed required for functionality. Matching the motor's performance characteristics with your project’s demands will lead to enhanced efficiency, reduced wear, and ultimately, a more successful implementation of the servo system.
When selecting servo motors for various projects, it's essential to understand the differences between analog and digital servo motor controllers. Analog controllers operate by sending a continuous signal to the servo, allowing for smooth and gradual movement. This control method works well for simpler applications where precision and response time are not critical. However, analog systems may struggle with faster response needs, particularly in dynamic environments, where they can exhibit lag or jitter due to noise in the signal.
On the other hand, digital servo motor controllers provide a more advanced solution by processing signals in discrete steps. This results in higher precision and faster response times, making them ideal for complex applications that require quick adjustments, such as robotics or CNC machinery. Digital controllers can also implement advanced features like PID control algorithms, improving stability and accuracy in performance. Ultimately, the choice between analog and digital controllers hinges on the specific requirements of the application, including the desired precision, speed, and complexity of control needed.
When budgeting for servo motors in your projects, it’s crucial to assess not only the initial cost of the motors but also their long-term value. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets,
the global servo motor market is projected to grow from $7.9 billion in 2023 to $12.6 billion by 2025, indicating a significant trend toward automation that highlights the growing importance of cost considerations in project planning. Investing in high-quality servo motors can reduce maintenance costs and downtime, ultimately leading to more efficient project execution.
Moreover, calculating the total cost of ownership (TCO) is essential in this process. The TCO encompasses not only the purchase price but also installation, operational, and maintenance expenses throughout the motor’s lifespan. A study from the International Society of Automation notes that investing in advanced servo systems can lead to operational savings of up to 30% compared to traditional motors due to their higher efficiency and precision. Therefore, while the upfront cost may appear higher, the financial benefits in terms of energy savings and reduced failure rates can justify the initial investment, reinforcing the importance of a comprehensive financial strategy when selecting servo motors for various applications.